Handle legacy audio archives and modern recordings with specialized transcription tools
Process multiple WMA files simultaneously to handle large audio collections
Automatic noise reduction and volume normalization for older or poor-quality recordings
Handle all WMA variants including WMA Pro, Lossless, and Voice codecs from any Windows version

Automatic paragraph breaks, punctuation, and number formatting for professional documents
Automated workflow designed for efficiency and accuracy
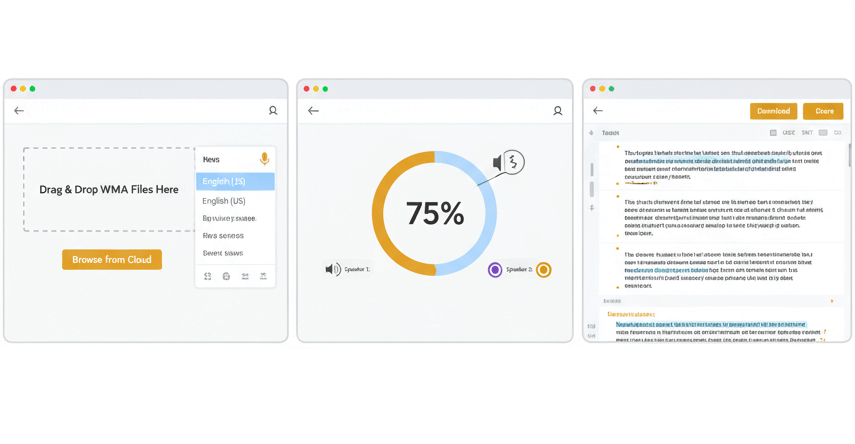
Drag WMA files directly into the browser or select from cloud storage. Specify the primary language spoken in the recording. The system automatically detects audio properties like bitrate and duration.
Speech recognition algorithms analyze audio patterns and convert spoken words into written text. Background noise gets filtered while preserving voice clarity. Multiple speakers are identified and labeled separately.
Access the completed transcript through an online editor for quick corrections. Download in standard document formats or specialized caption files. All original timestamps remain linked for audio synchronization.
Microsoft's proprietary audio codec widely used in Windows environments and enterprise systems
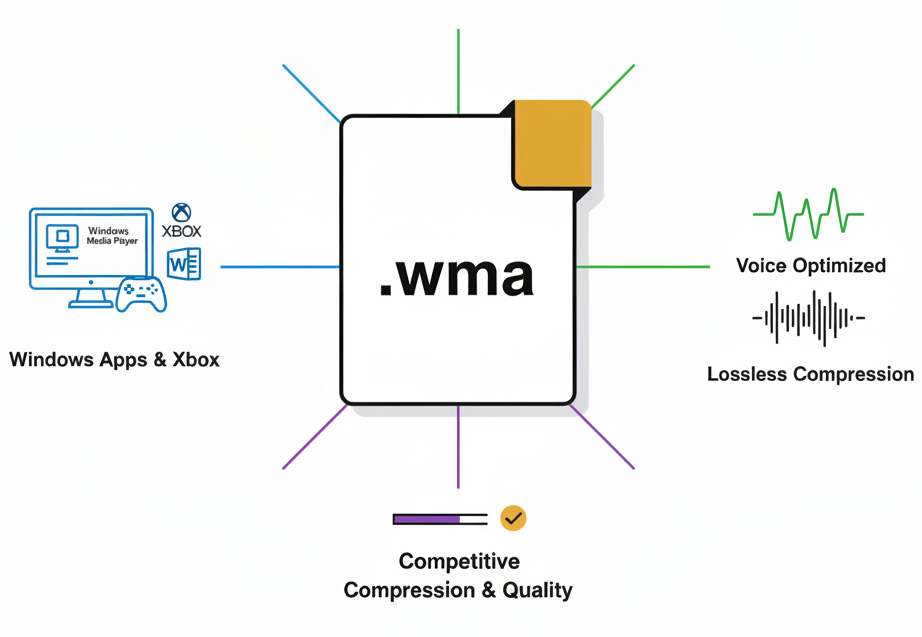
Windows Media Audio emerged as Microsoft's answer to MP3, offering competitive compression rates and sound quality. Files carry the .wma extension and integrate with Windows Media Player, Xbox systems, and various Microsoft applications. Different encoding profiles exist, from voice-optimized to lossless compression.
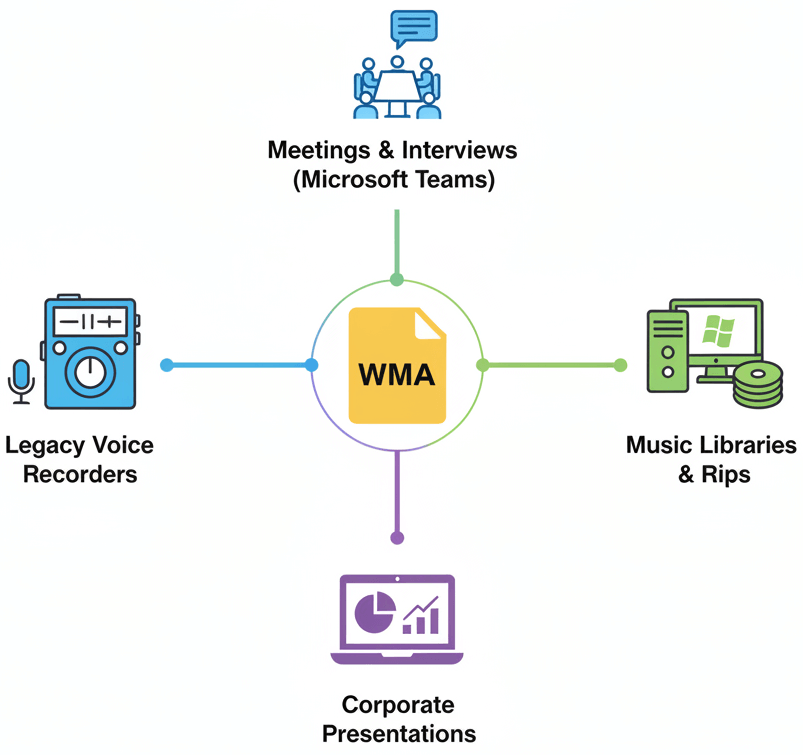
Corporate presentations recorded through Windows systems often default to WMA. Legacy voice recorders from the 2000s frequently saved in this format. Music libraries ripped using older Windows Media Player versions contain extensive WMA collections. Many organizations store years of meetings, interviews, and recordings in WMA format. Microsoft Teams recordings and Windows Media Player rips often default to WMA.
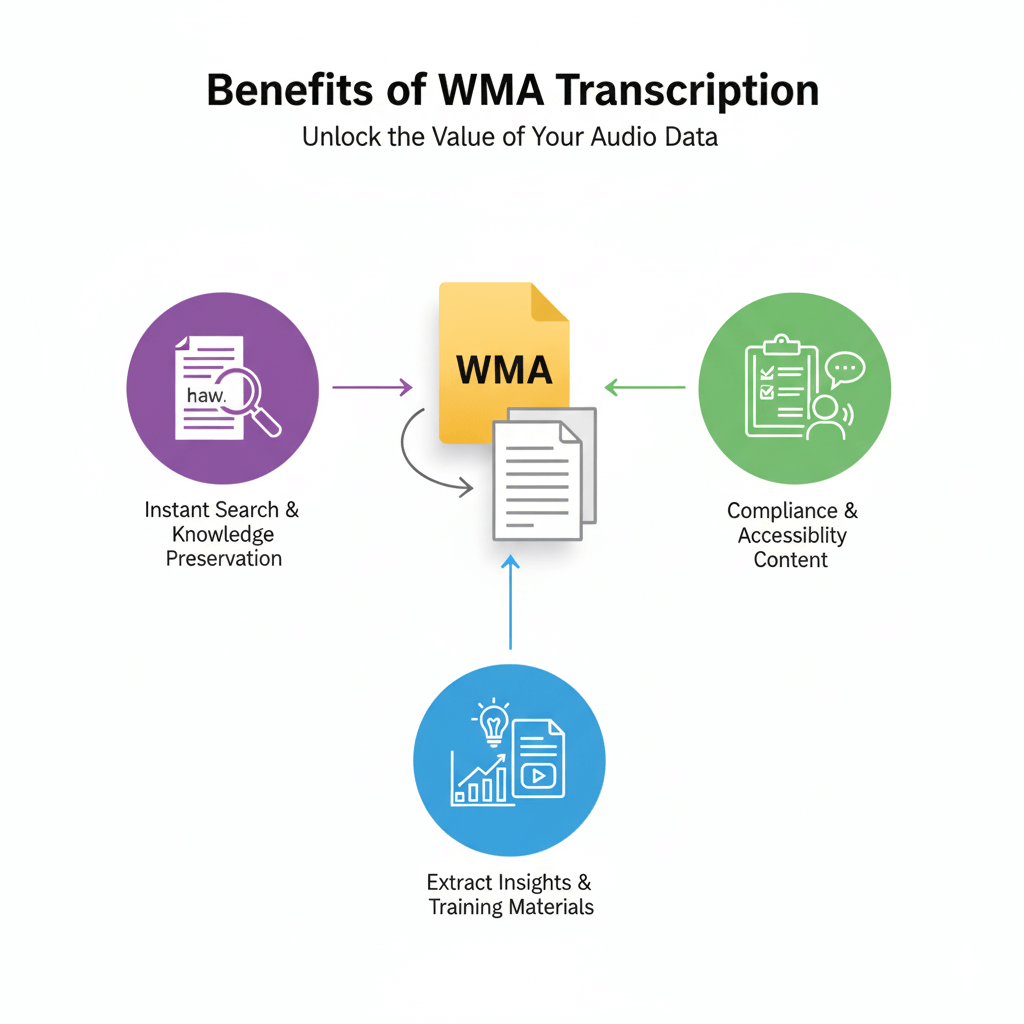
Text transcripts enable instant searching across years of recordings, compliance documentation, and knowledge preservation. Organizations can convert audio content for training materials, extract insights from customer calls, and create accessible versions of audio-only content. Companies discover insights from years of stored audio that remained inaccessible until transcribed into readable documents.
Real-world applications of WMA transcription across industries and departments
Legacy WMA recordings from older devices work well with modern transcription engines. Audio enhancement features automatically improve clarity before processing begins. Even compressed WMA files from early 2000s devices produce reliable transcripts.
Trial accounts process standard-length WMA recordings without restrictions. Extended recordings like multi-hour meetings or conferences may require paid plans for complete transcription. File size limits depend on audio duration rather than compression settings.
All standard WMA formats process successfully, including WMA Standard, WMA Professional, and WMA Lossless. Variable bitrate (VBR) and constant bitrate (CBR) encodings both convert properly. Files from any Windows version or recording device are processed accurately regardless of compression settings or bitrate. DRM-protected files require removal of protection before transcription.
Processing speed depends on recording length and audio complexity. Typical one-hour WMA files complete transcription within 15-20 minutes. Clear audio transcribes faster than recordings with background noise.
Enterprise-grade encryption protects files during upload, processing, and storage. Automatic deletion policies, access controls, and audit logs ensure compliance with corporate data handling requirements. Processing occurs on isolated infrastructure with no human access to content.